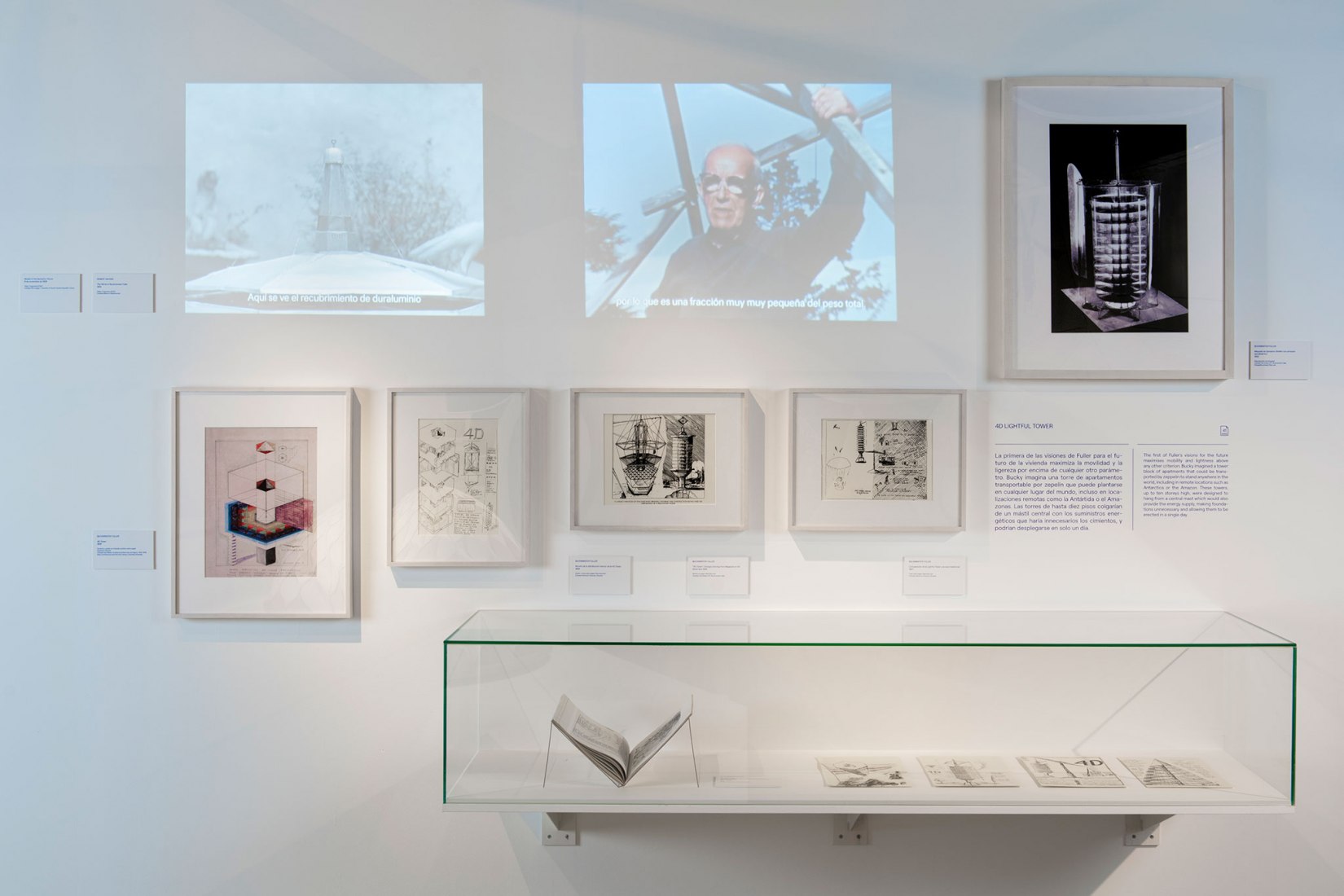
A journey into the mind of Richard Buckminster Fuller, an American designer, architect, thinker, philosopher and visionary.We invite you to rethink the future and imagine a world based on more sustainable principles. On floor 3 of the Espacio Fundación Telefónica between September 16, 2020 and March 14, 2021.
The exhibition delves into Fuller's universe in a context of transformation and emergence since the beginning of the 21st century, going through his main research, innovation and development works based on his ideas.
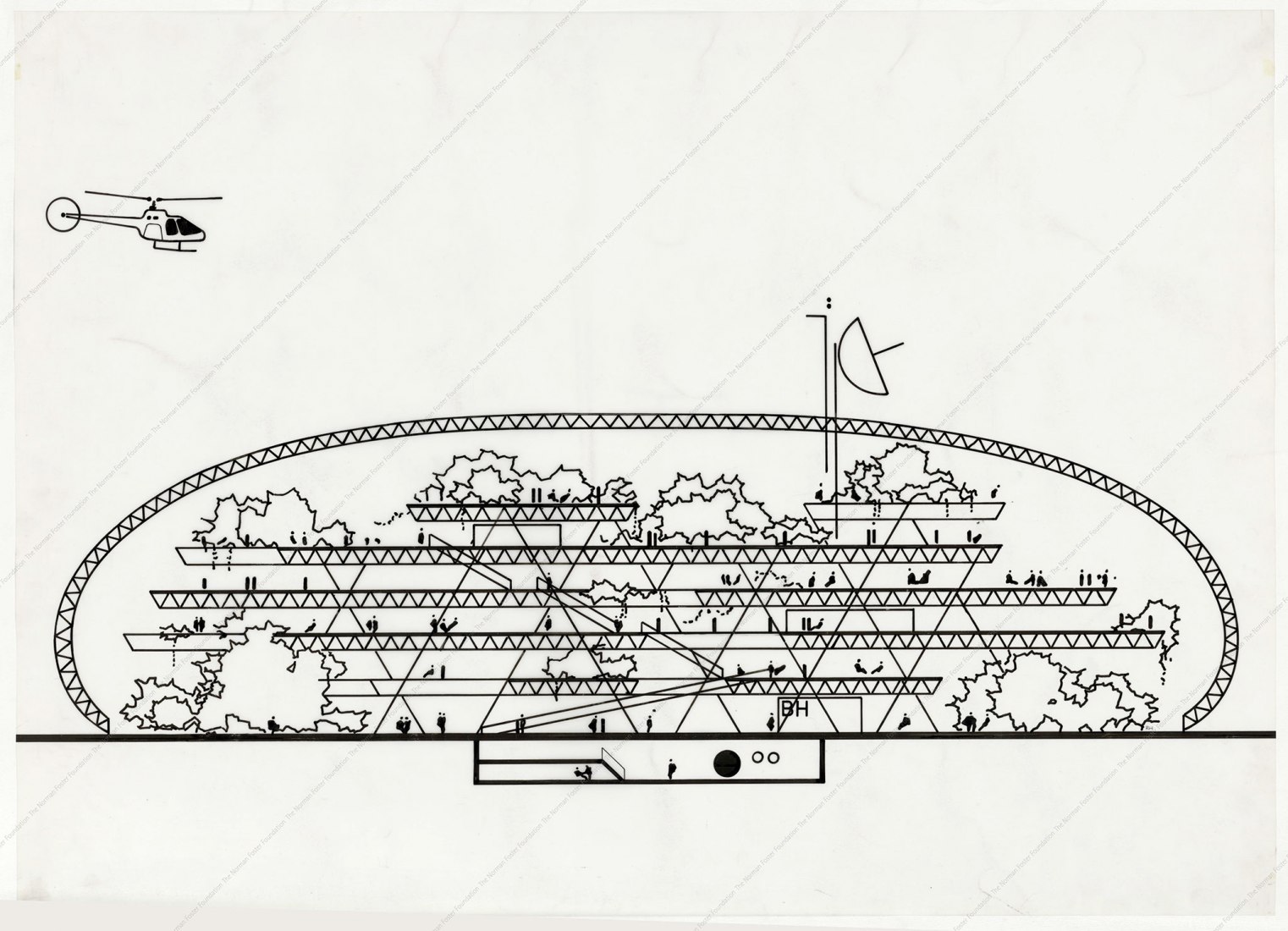
The exhibition also includes proposals from contemporary and contemporary artists who applied their ideas in architecture, art and design. A group of characters among which we can include architects like Abeer Seikaly, Norman Foster and Chuck Hoberman, designers Neri Oxman and Joris Laarman, or artists Olafur Eliasson, Ruth Asawa and Tomáš Libertíny.
The exhibition delves into Fuller's universe in a context of transformation and emergence since the beginning of the 21st century, going through his main research, innovation and development works based on his ideas.
The exhibition also includes proposals from contemporary and contemporary artists who applied their ideas in architecture, art and design. A group of characters among which we can include architects like Abeer Seikaly, Norman Foster and Chuck Hoberman, designers Neri Oxman and Joris Laarman, or artists Olafur Eliasson, Ruth Asawa and Tomáš Libertíny.
“My ideas have undergone a process of emergence by emergency. When they are needed badly enough, they are accepted.”
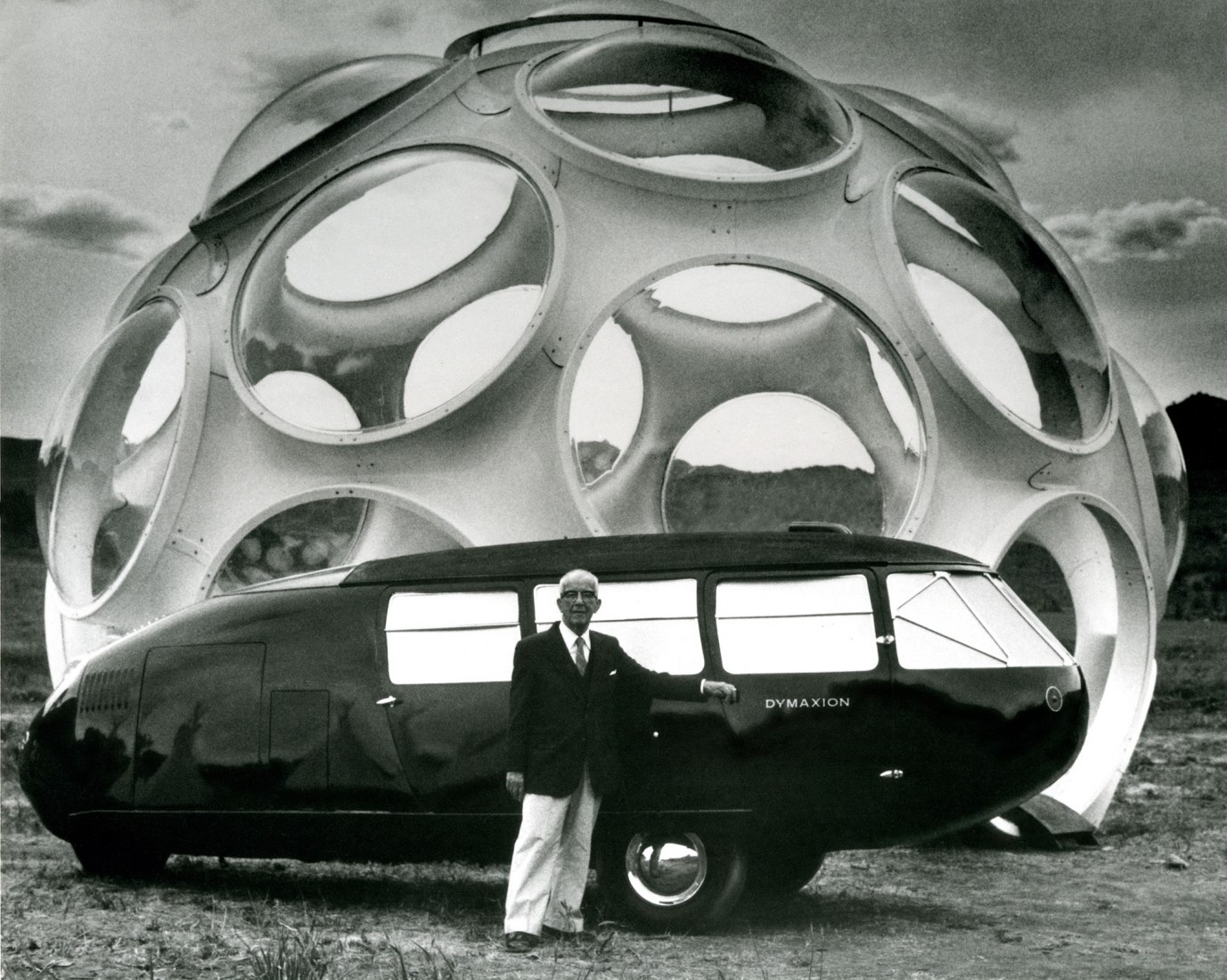
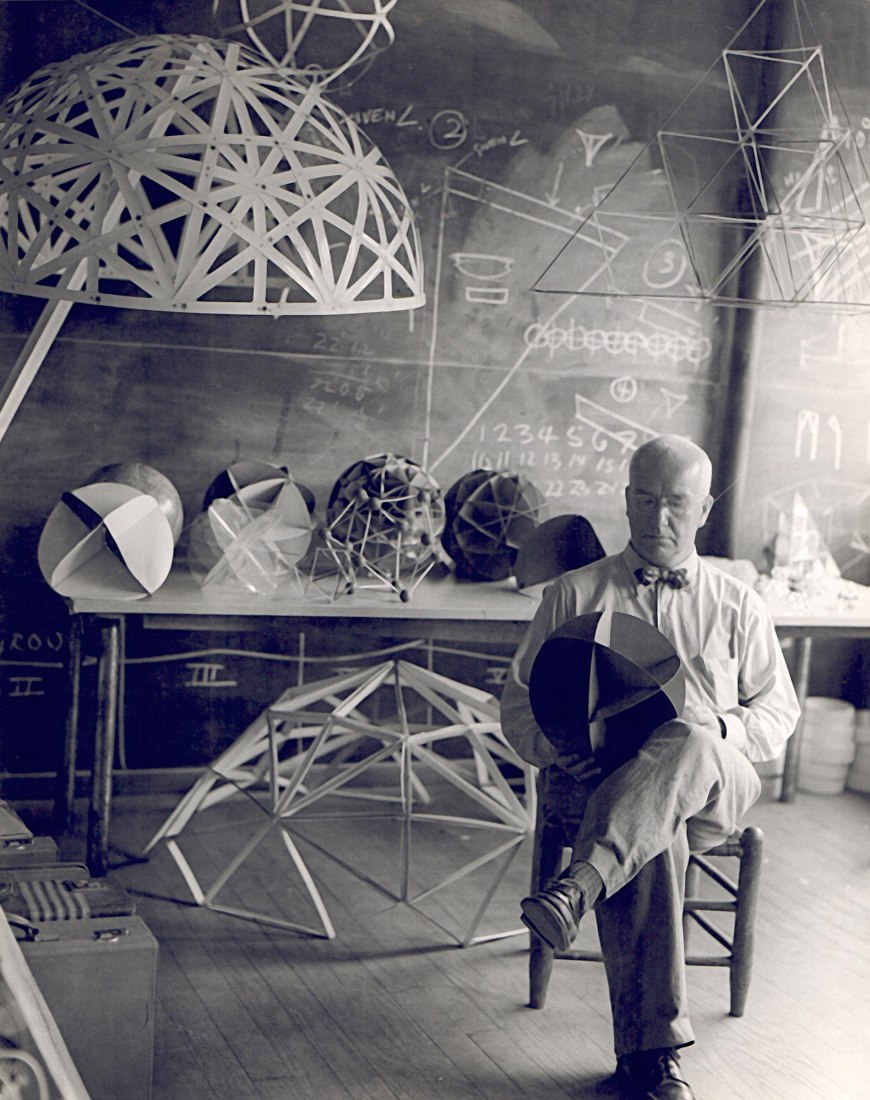
For some, Fuller was the Leonardo da Vinci of the 20th century. Richard Buckminster Fuller (1895-1983)dedicated his life to finding solutions that would ensure that the world worked better for everybody. Through his thinking,he was able to anticipate some of the major crises of the 20th century surprisingly accurately.
A virtually unclassifiable visionary and investigator, Fuller created a seemingly never-ending body of work that crossed over disciplines such as architecture, engineering, philosophy and education, through a vision of design that was capable of changing the world.From questions of mobility and housing to education and the use of big data, his thinking included a number of questions that Covid-19 has put at the very heart of the world’s agenda.
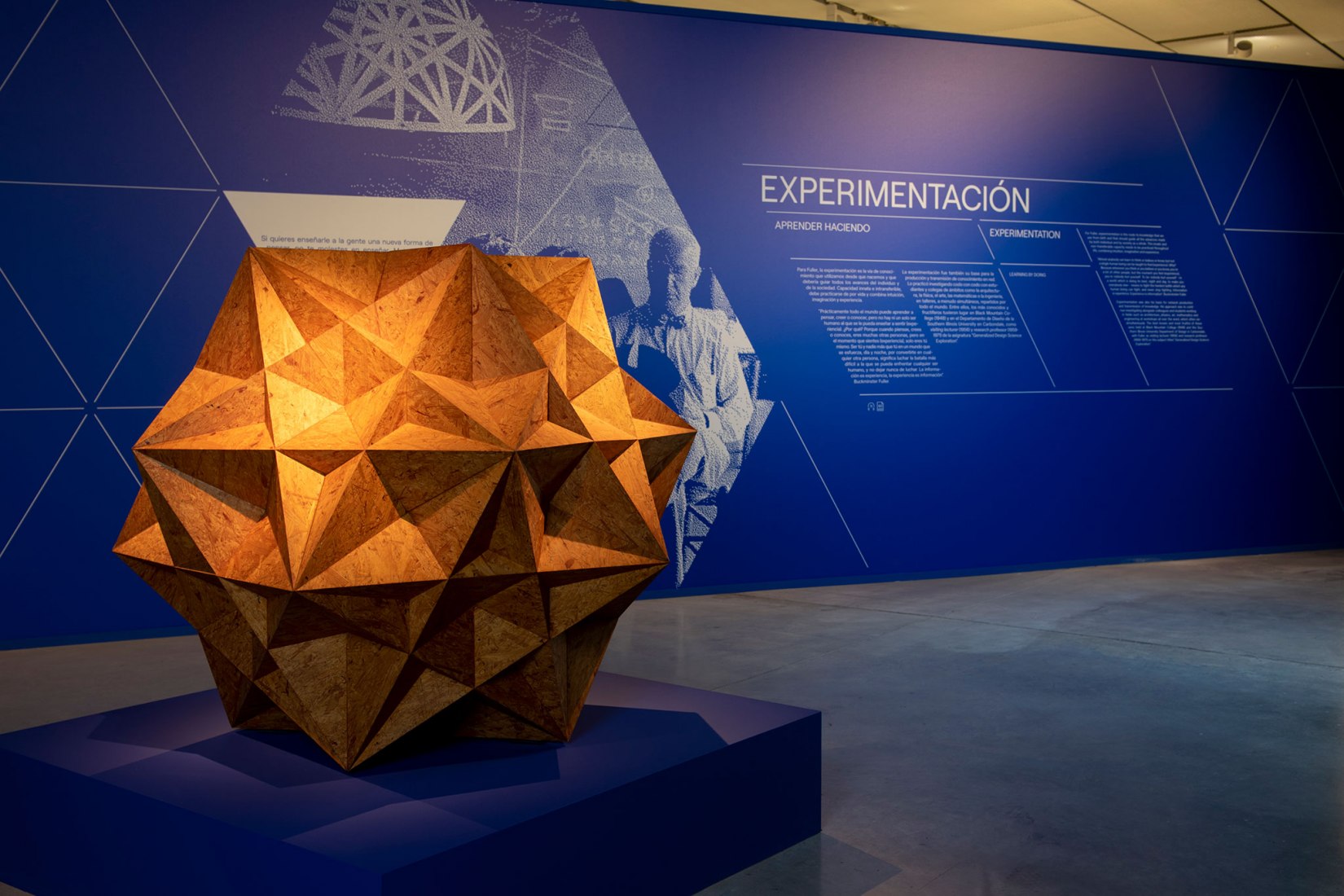
The power of experimentation
Even though we are not experts, we are all capable of doing incredible things. Fuller’s starting point was this powerful idea. He saw experimentation as the way to the knowledge which we have all used since we were born and which guide us in the advances we make as individual and as a society. An innate ability that combines intuition, imagination and experience.
Fuller experimented tirelessly throughout his life, defining himself as a kind of scientific designer – actually a “comprehensive anticipatory design scientist” – and vice-versa. His mission: “To make the world work for 100% of humanity in the shortest possible time through spontaneous cooperation without ecological offense or the disadvantage of anyone.”
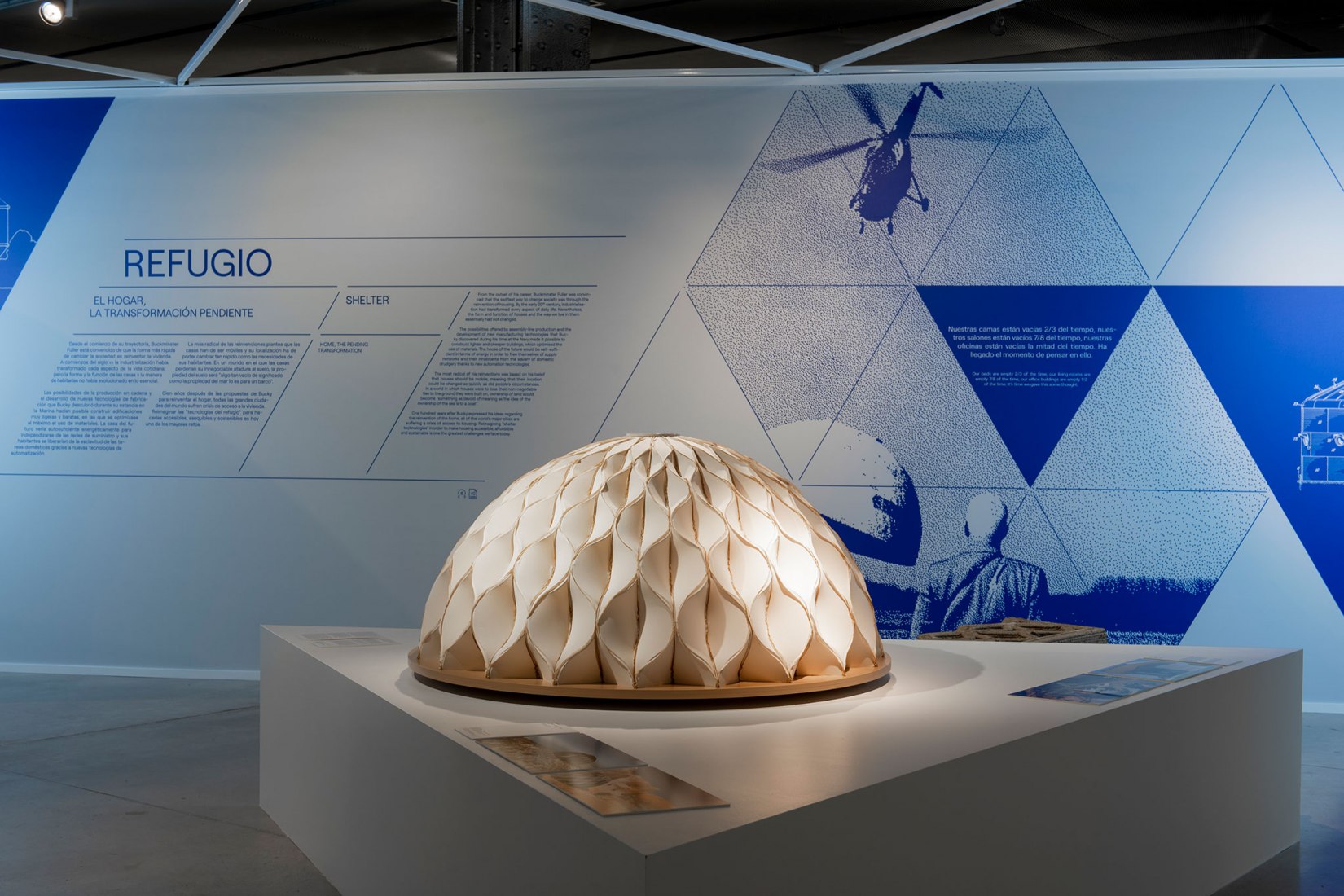
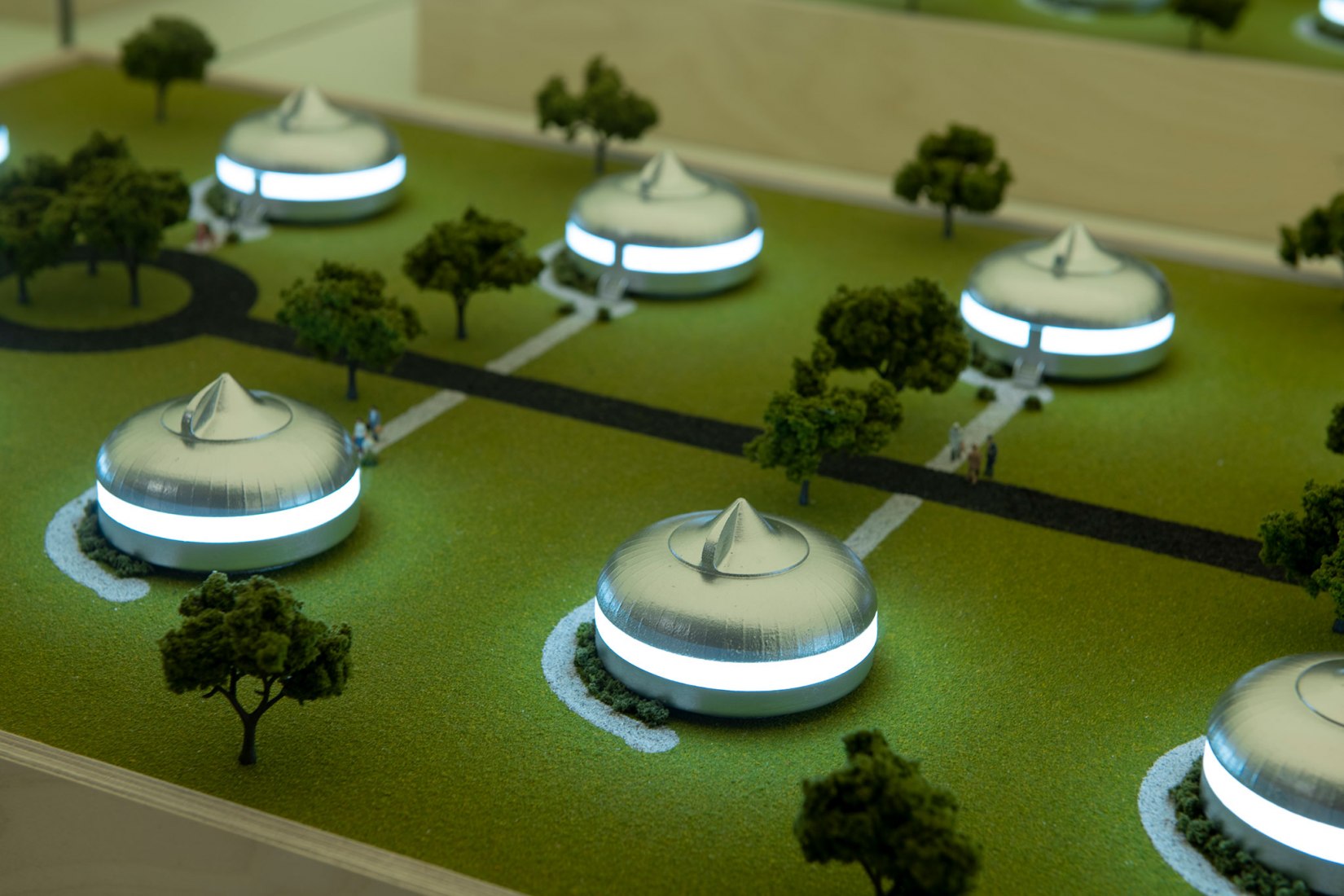
Lightness, adaptability and mobility. His main concerns focused on housing and cars, resulting in his revolutionary Dymaxion House and Dymaxion Car. That’s where it all began for him, changing society. A hundred years later, access to affordable and sustainable housing is still a challenge for the world’s big cities.
The forces that govern the universe
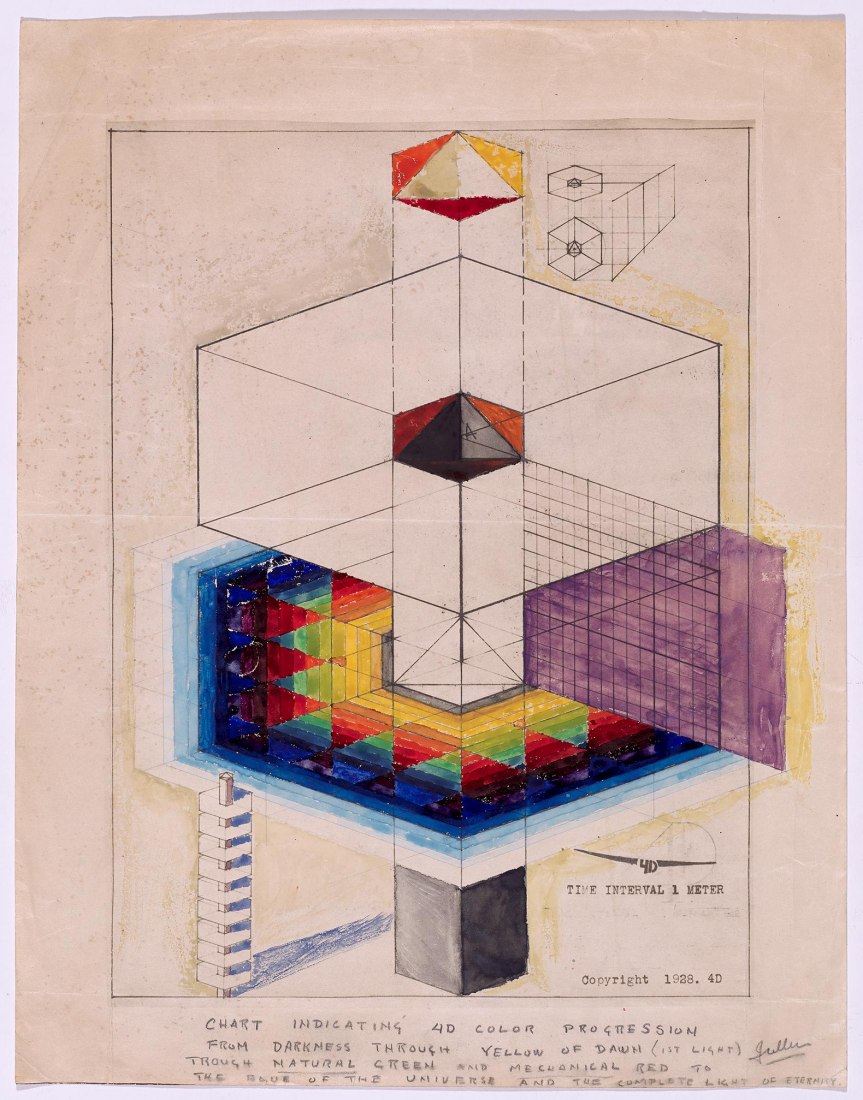
The foundations of Fuller’s philosophy include the idea of ‘synergy’. He saw the universe as a “synergy-of-synergies”, complete systems that cannot be predicted by observing its part separately, as “there is nothing that one does that does not affect all others to a varying extent. This can be applied to all life forms.”
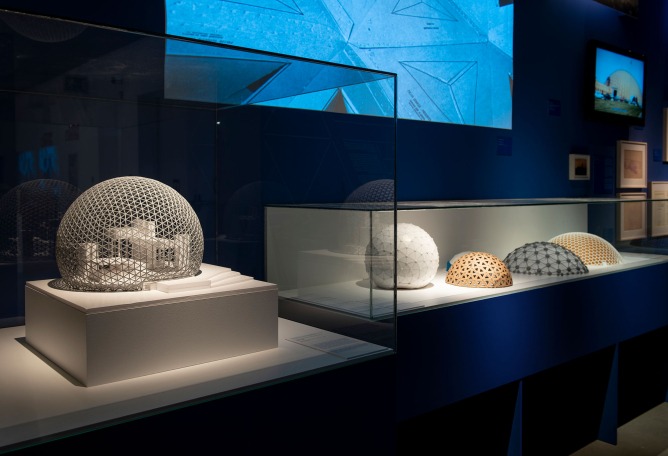
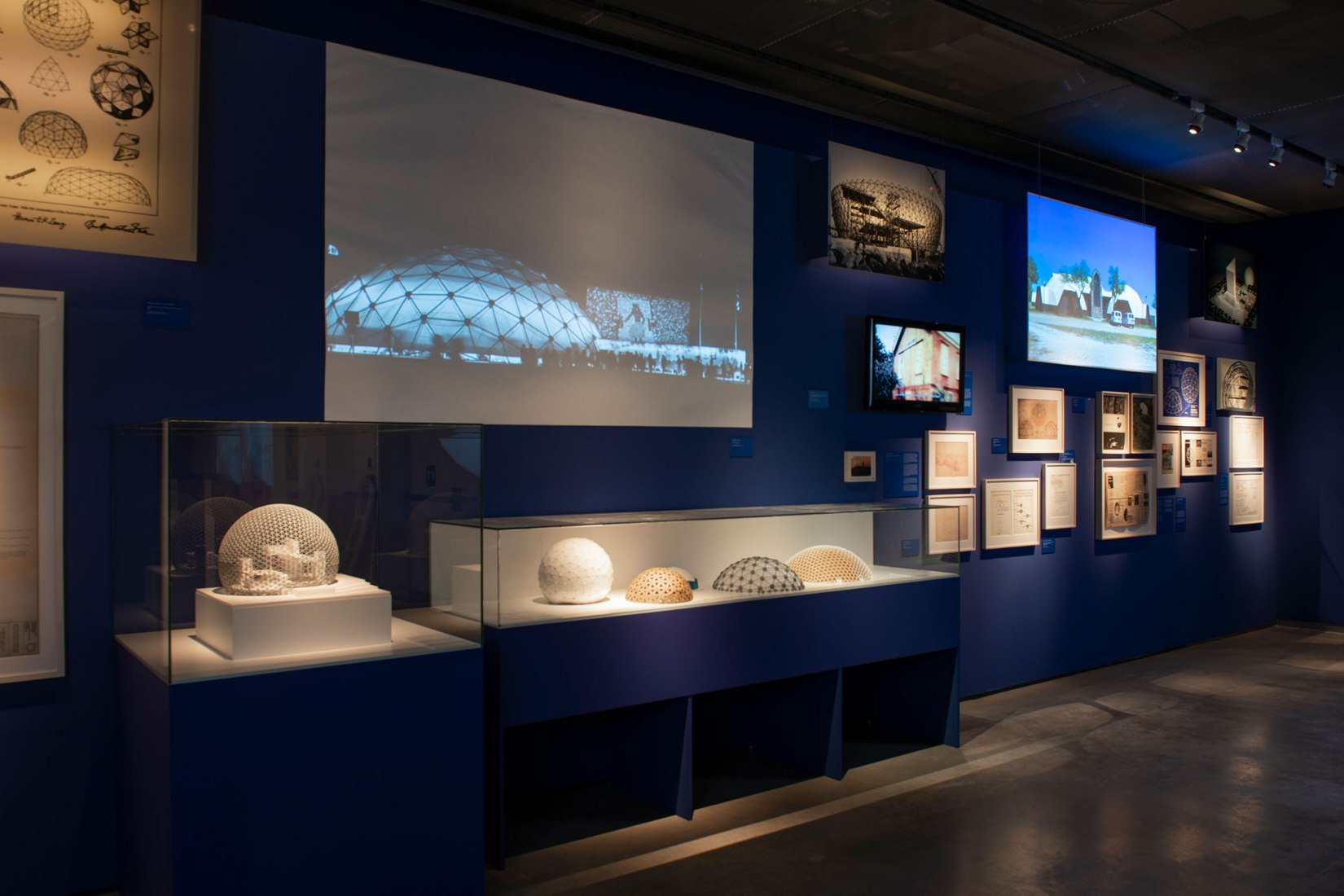
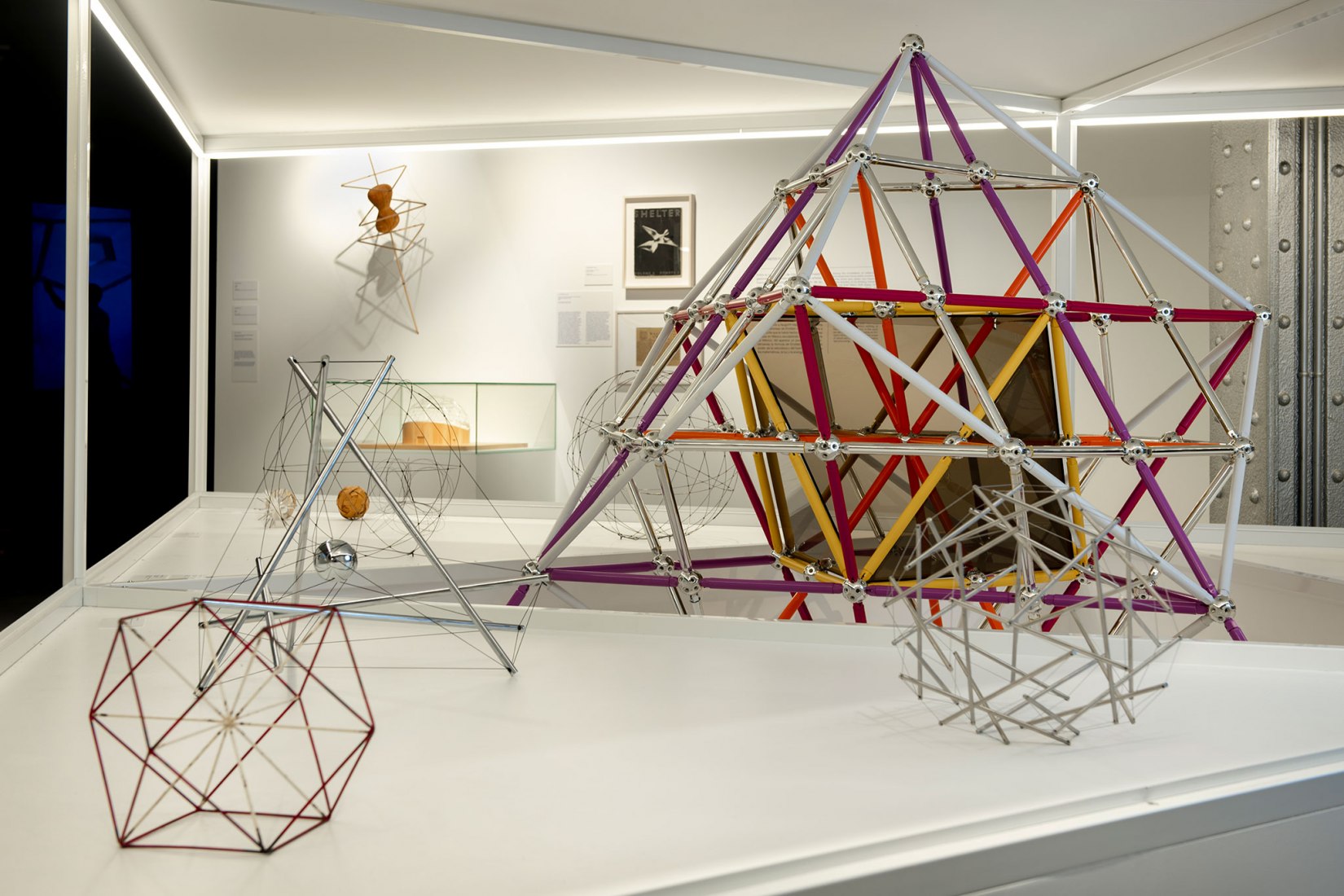
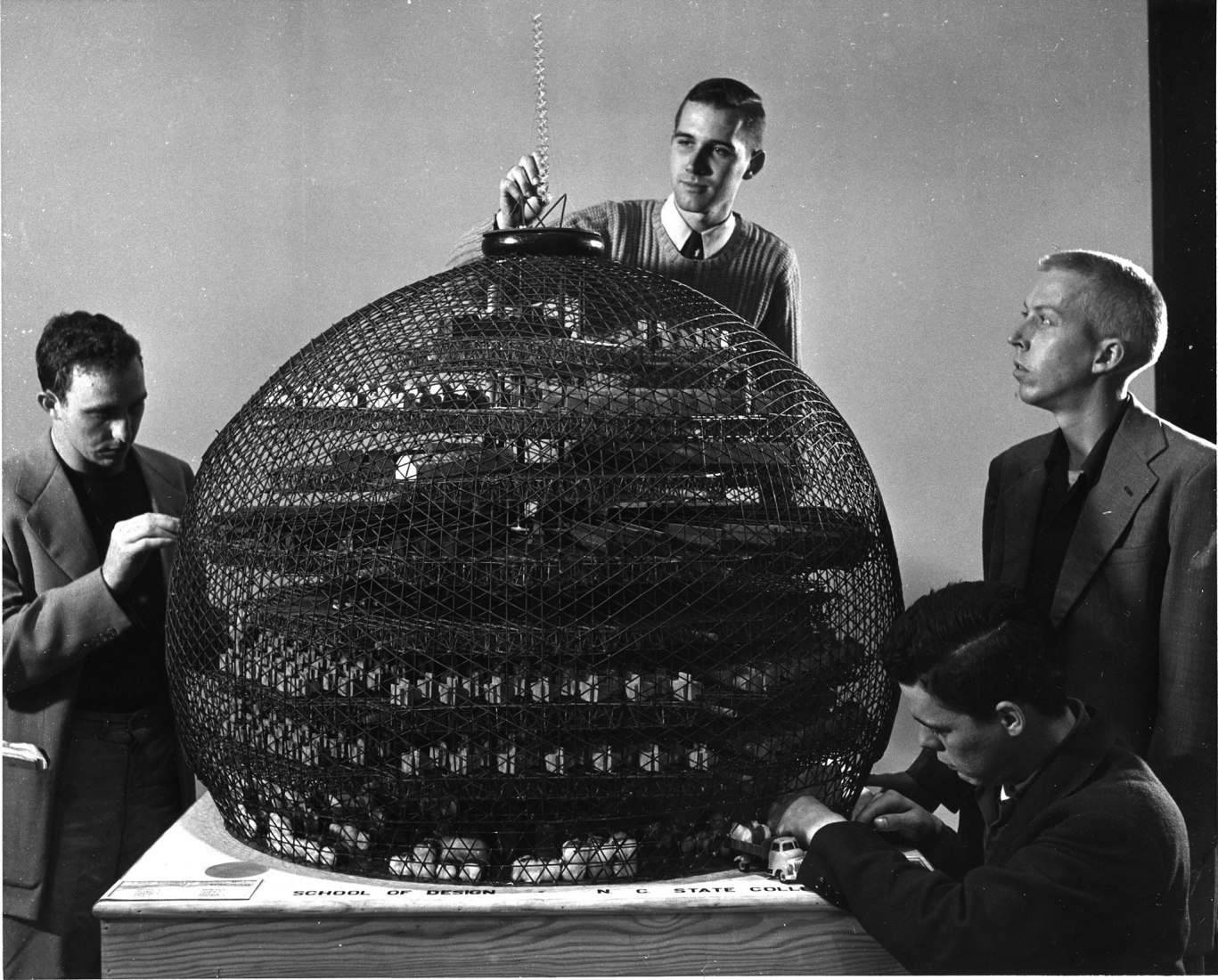
In his approach to visualisation, Fuller applied geometry, giving rise to another of his key concepts – “tensegrity”, a structural principle that combines “tension” and “integrity”. In the 1950s, his investigations into tensegrity and his obsessive study of geometric laws converged in his most successful project, which was to represent the United States at the 1967 Universal Exhibition, becoming an iconic image of the future for decades to come – the geodesic dome, the greatest area that can be covered with the least amount of material and which can support itself without the need for foundations. It is impossible to do more with less.
These ideas of synergy and efficiency made Fuller a pioneer of environmental awareness. His calls to act responsibly in order to not risk the future of “Spaceship Earth”, foresaw the modern idea of sustainability.
“It’s impossible to know less. You can only know more”
Fuller’s revolution would also impact on the world of education. Given our innate abilities to understand “Spaceship Earth”, he saw it as essential to eradicate educational programmes that repress curiosity and our natural inclination to experimentation. He also advocated for technological devices that improve concentration and communication. Among his inventions designed to strengthen learning, his Geoscope and Dymaxion Map are worthy of special mention..
Fuller took the view that the origin of many problems are due to a lack of information and the inability to detect patters in society and the economy. He felt that with sufficient information, it would be easier to find solutions. With his defence of the design-science duality, Fuller foresaw current conversations regarding big data, data visualisation and gamification in order to tackle complex problems.
More information
Published on:
September 15, 2020
Cite:
"Radical curiosity. In the orbit of Buckminster Fuller. Opening" METALOCUS.
Accessed
<https://www.metalocus.es/en/news/radical-curiosity-orbit-buckminster-fuller-opening>
ISSN 1139-6415
Loading content ...
Loading content ...
Loading content ...
Loading content ...
Loading content ...
Loading content ...
Loading content ...
Loading content ...
Loading content ...
Loading content ...
Loading content ...
Loading content ...
Loading content ...
Loading content ...
Loading content ...
Loading content ...
Loading content ...
Loading content ...
Loading content ...
Loading content ...
Loading content ...
Loading content ...
Loading content ...
Loading content ...
Loading content ...
Loading content ...
Loading content ...
Loading content ...
Loading content ...
Loading content ...
Loading content ...
Loading content ...
Loading content ...
Loading content ...
Loading content ...
Loading content ...
Loading content ...
Loading content ...
Loading content ...
Loading content ...
Loading content ...
Loading content ...
Loading content ...
Loading content ...
Loading content ...
Loading content ...
Loading content ...
Loading content ...
Loading content ...
Loading content ...
Loading content ...
Loading content ...
Loading content ...
Loading content ...